n8n v2.0 breaking changes#
n8n v2.0 will be released soon. This document highlights important breaking changes and actions you should take to prepare for the transition. These updates improve security, simplify configuration, and remove legacy features.
The release of n8n 2.0 continues n8n's commitment to providing a secure, reliable, and production-ready automation platform. This major version includes important security enhancements and cleanup of deprecated features.
Behavior changes#
Return expected sub-workflow data when the sub-workflow resumes from waiting (waiting for webhook, forms, HITL, etc.)#
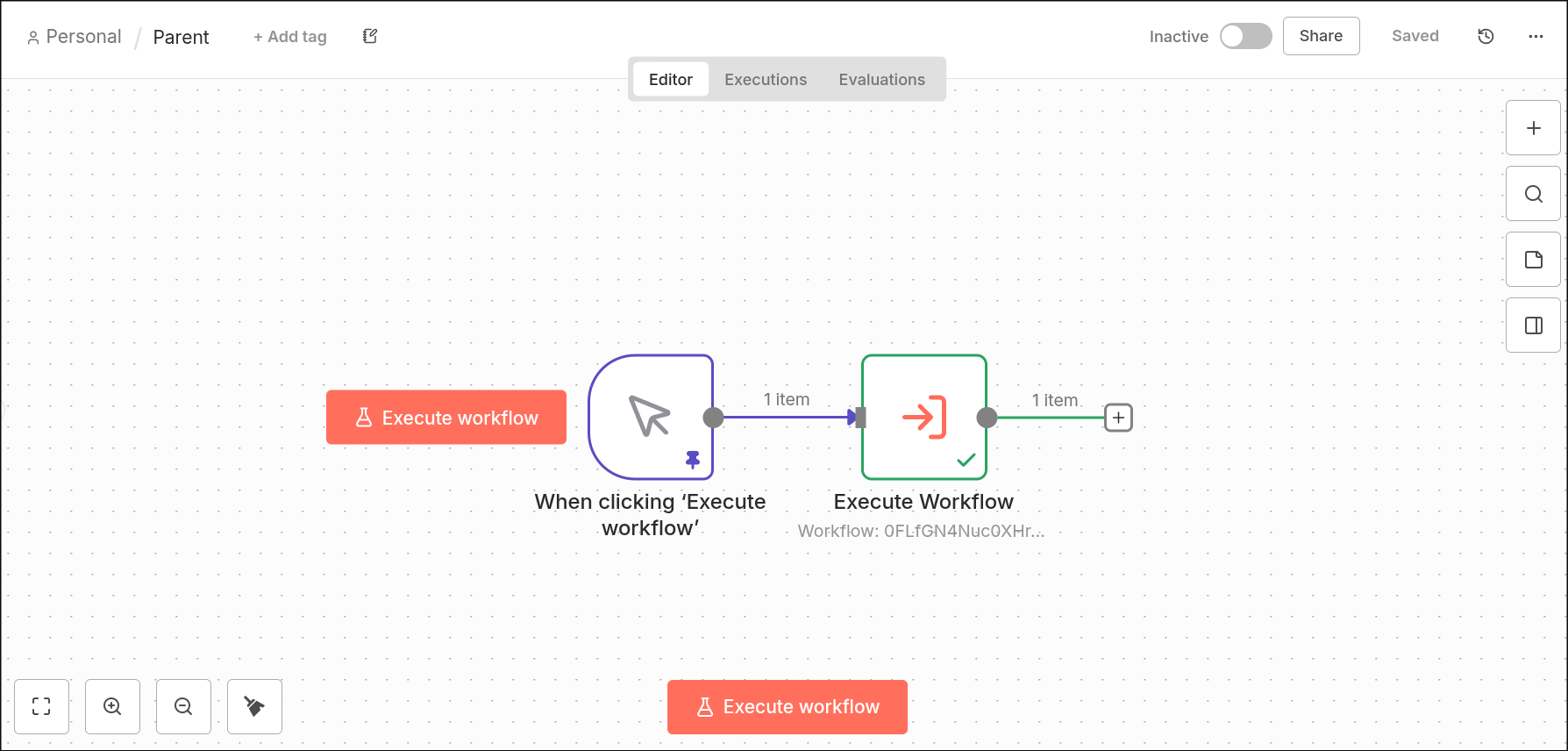
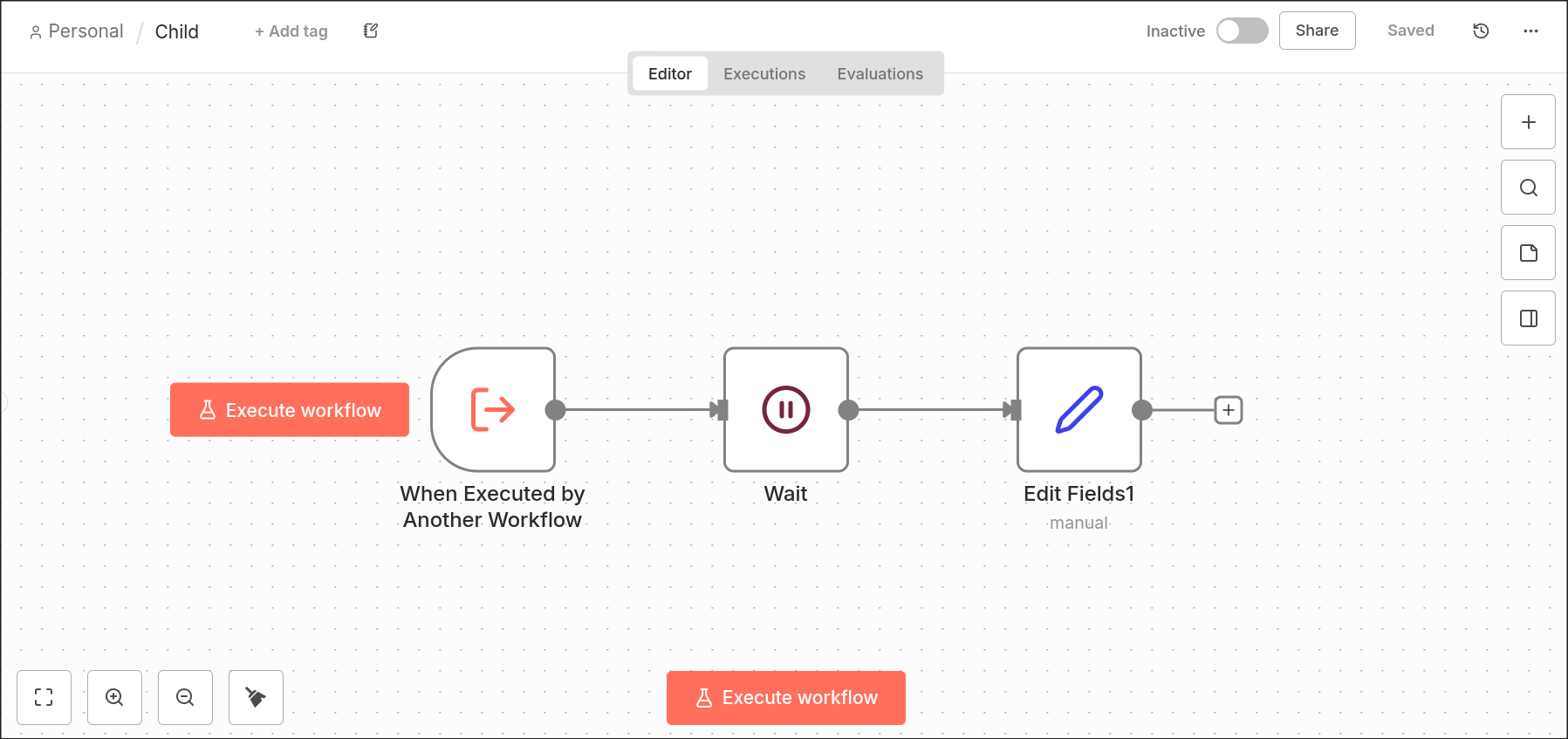
Previously, when an execution (parent) called a sub-execution (child) that contained a node that causes the sub-execution to enter the waiting state and the parent-execution is set up to wait for the sub-execution's completion, the parent-execution would receive incorrect results.
Entering the waiting state would happen for example if the sub-execution contains a Wait node with a timeout higher than 65 seconds or a webhook call or a form submission, or a human-in-the-loop node, like the slack node.
v1: The parent-execution reproduces the sub-execution's input as its output.:
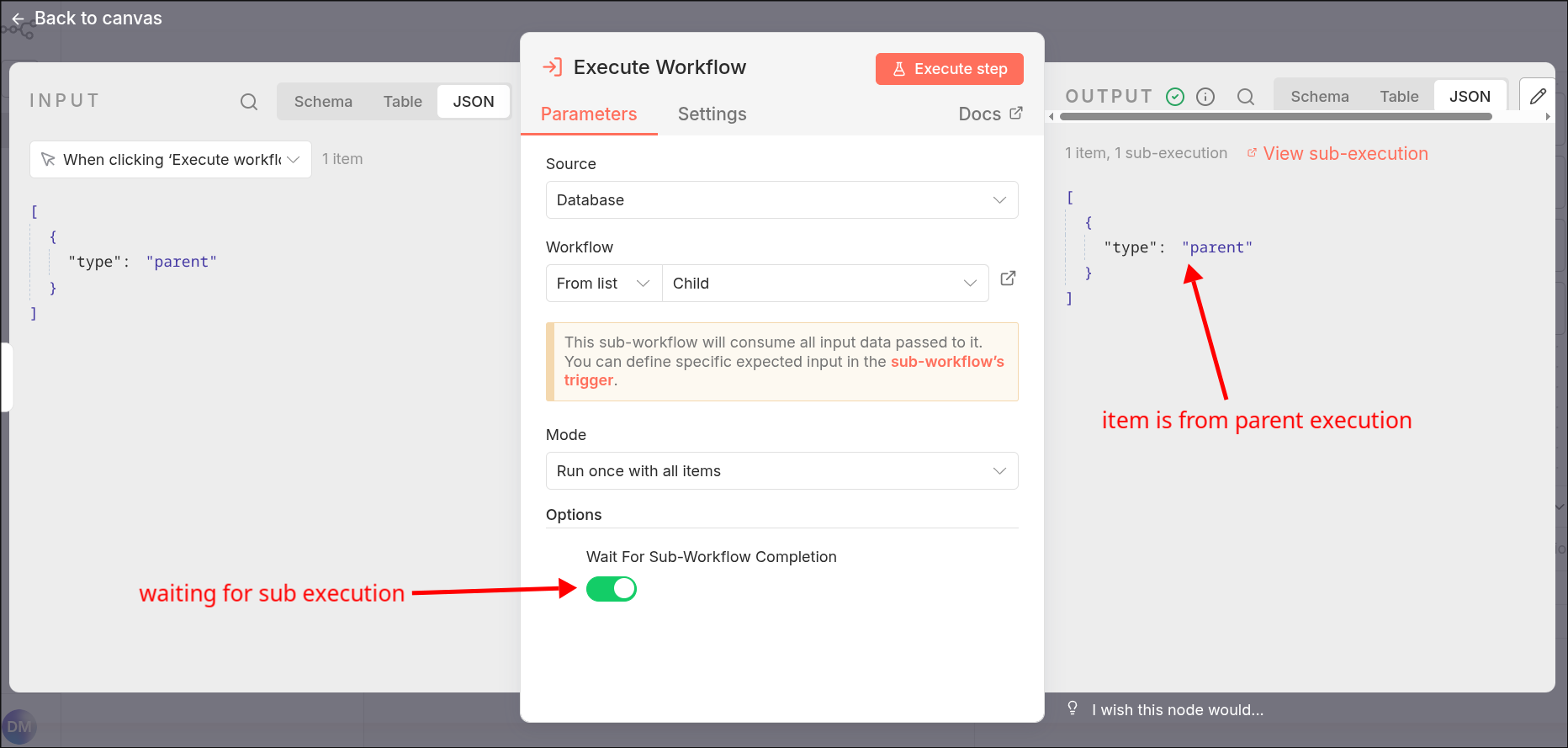
v2: The parent execution receives the result of the child execution:
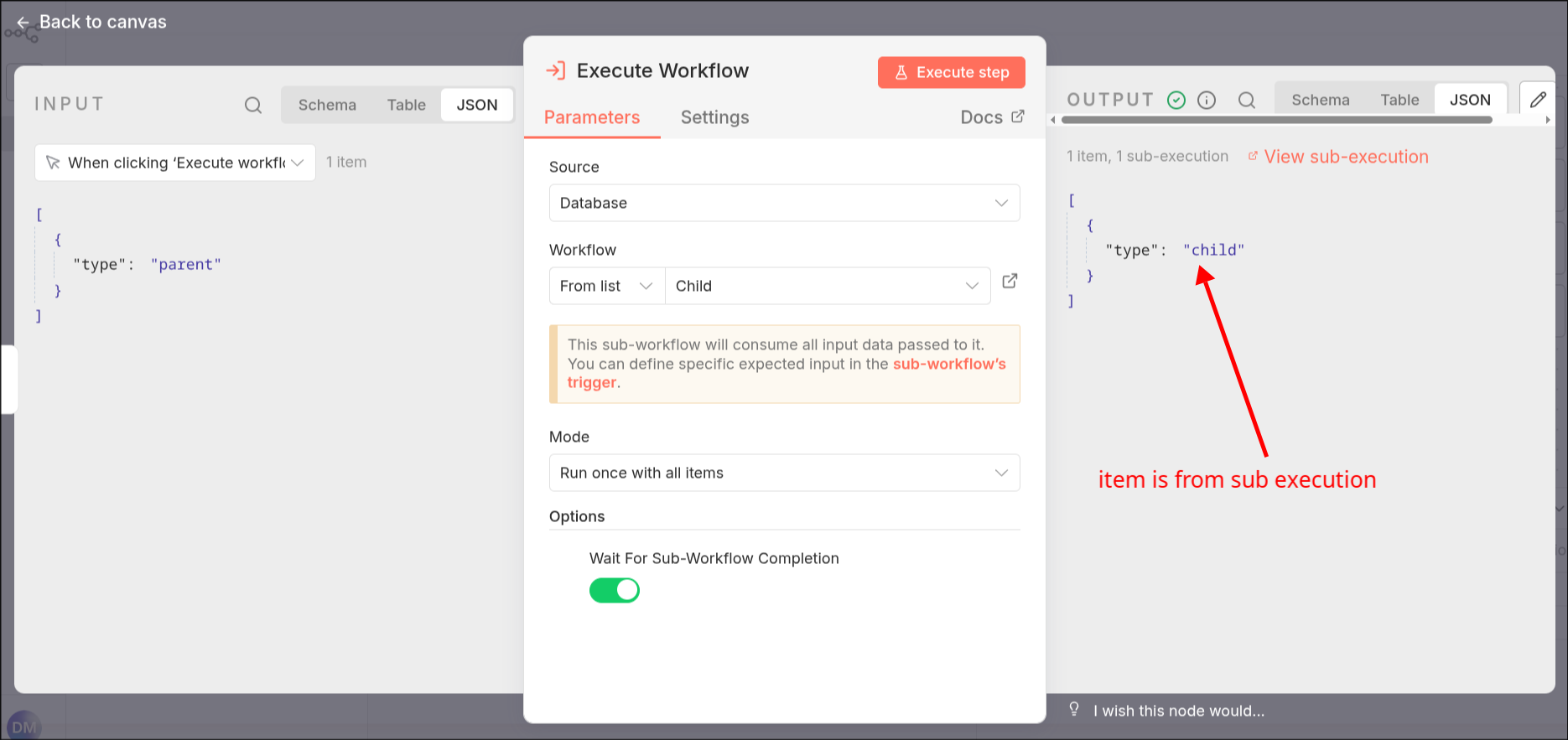
This allows using human-in-the-loop nodes in the sub-workflow and use the results (for example approving or declining an action) in the parent-workflow.
Migration path: Review any workflows that call sub-workflows and expect to receive the input to the sub-workflow. Update these workflows to handle the new behavior, where the parent-workflow receives the output from the end of the child-workflow instead.
Start node removed#
The Start node is no longer supported. This node was the original way to begin workflows but more specific trigger nodes now replace it.
Migration path: Replace the Start node based on how you use your workflow:
- Manual executions: Replace the Start node with a Manual Trigger node.
- Sub-workflows: If another workflow calls this workflow as a sub-workflow, replace the Start node with an Execute Workflow Trigger node and activate the workflow.
- Disabled Start nodes: If the Start node is disabled, delete it from the workflow.
Saving and publishing workflows#
The new workflow publishing system replaces the previous active/inactive toggle. This means that the old "Activate/Deactivate" toggles become the new "Publish/Unpublish" buttons. This change gives you better control over when your workflow changes go live, reducing the risk of accidentally deploying work-in-progress changes to production. More information can be found here: Saving and publishing workflows.
Removed nodes for retired services#
The following nodes have been removed because the external services they connect to are no longer available:
- Spontit node
- crowd.dev node
- Kitemaker node
- Automizy node
Migration path: If your workflows use any of these nodes, update or remove those workflows to avoid errors.
Security#
Block environment variable access from Code Node by default#
To improve security, n8n will block access to environment variables from the Code node by default. The default value for N8N_BLOCK_ENV_ACCESS_IN_NODE is now set to true.
Migration path: If your workflows require access to environment variables in Code nodes, set N8N_BLOCK_ENV_ACCESS_IN_NODE=false in your environment configuration. For sensitive data, use credentials or other secure methods instead of environment variables.
Enforce settings file permissions#
n8n will require strict file permissions for configuration files to improve security. By default, configuration files must use 0600 permissions, which means only the file owner can read and write them. This approach is similar to how SSH protects private keys.
Migration path: To test this behavior before v2.0, set N8N_ENFORCE_SETTINGS_FILE_PERMISSIONS=true. If your environment doesn't support file permissions (for example, on Windows), set N8N_ENFORCE_SETTINGS_FILE_PERMISSIONS=false to disable this requirement.
Enable task runners by default#
n8n will enable task runners by default to improve security and isolation. All Code node executions will run on task runners.
Migration path: Before upgrading to v2.0, set N8N_RUNNERS_ENABLED=true to test this behavior. Make sure your infrastructure meets the requirements for running task runners. For additional security, consider using external mode.
Remove task runner from n8nio/n8n docker image#
Starting with v2.0, the main n8nio/n8n Docker image will no longer include the task runner for external mode. You must use the separate n8nio/runners Docker image to run task runners in external mode.
Migration path: If you run task runners in Docker with external mode, update your setup to use the n8nio/runners image instead of n8nio/n8n.
Remove Pyodide-based Python Code node and tool#
n8n will remove the Pyodide-based Python Code node and tool and replace them with a task runner-based implementation that uses native Python for better security and performance. Starting in v2.0, you can only use Python Code nodes with task runners in external mode and native Python tools.
The native Python Code node doesn't support built-in variables like _input or dot access notation, which were available in the Pyodide-based version. For details, see the Code node documentation.
The native Python tool supports _query for the input string that the AI Agent passes to the tool when it calls it.
Migration path: To continue using Python in Code nodes, set up task runners in external mode and review your existing Python Code nodes and tools for compatibility.
Disable ExecuteCommand and LocalFileTrigger nodes by default#
n8n will disable the ExecuteCommand and LocalFileTrigger nodes by default because they pose security risks. These nodes allow users to run arbitrary commands and access the file system.
Migration path: If you need to use these nodes, remove them from the disabled nodes list in your n8n configuration by updating the NODES_EXCLUDE environment variable. For example, set NODES_EXCLUDE="[]" to enable all nodes, or remove only the specific nodes you need.
Require authentication on OAuth callback URLs by default#
n8n will require authentication for OAuth callback endpoints by default. The default value for N8N_SKIP_AUTH_ON_OAUTH_CALLBACK will change from true (no authentication required) to false (authentication required).
Migration path: Before upgrading to v2.0, set N8N_SKIP_AUTH_ON_OAUTH_CALLBACK=false and test your OAuth integrations to ensure they work with authentication enabled.
Set default value for N8N_RESTRICT_FILE_ACCESS_TO#
n8n will set a default value for N8N_RESTRICT_FILE_ACCESS_TO to control where file operations can occur. This affects the ReadWriteFile and ReadBinaryFiles nodes. By default, these nodes can only access files in the ~/.n8n-files directory.
Migration path: Review your workflows that use file nodes and make sure they only access files in the allowed directory. If you need to allow access to other directories, set the N8N_RESTRICT_FILE_ACCESS_TO environment variable to your desired path.
Change the default value of N8N_GIT_NODE_DISABLE_BARE_REPOS to true#
By default, the Git node will now block bare repositories for security reasons. The default value for N8N_GIT_NODE_DISABLE_BARE_REPOS is set to true, which means bare repositories are disabled unless you change this setting.
Migration path: If your workflows need to use bare repositories, set N8N_GIT_NODE_DISABLE_BARE_REPOS=false in your environment configuration to enable them.
Data#
Drop MySQL/MariaDB support#
n8n will no longer support MySQL and MariaDB as storage backends. This support was deprecated in v1.0. For best compatibility and long-term support, use PostgreSQL. MySQL node will continue to be supported as before.
Migration path: Before upgrading to v2.0, use the database migration tool to move your data from MySQL or MariaDB to PostgreSQL or SQLite.
Remove SQLite legacy driver#
n8n will remove the legacy SQLite driver due to reliability issues. The pooling driver will become the default and only SQLite driver. The pooling driver uses WAL mode, a single write connection, and a pool of read connections. Our benchmarks show it can be up to 10 times faster.
Migration path: The sqlite-pooled driver will become the default automatically. You can enable pooling now by setting DB_SQLITE_POOL_SIZE to a value greater than 0. The default pool size will be set to 2.
Remove in-memory binary data mode#
n8n will remove the default mode for N8N_DEFAULT_BINARY_DATA_MODE, which keeps execution binary data in memory during execution. For better performance and stability the following options will be available starting from v2:
filesystem: Binary data is stored in the filesystem. Default option in regular mode.database: Binary data is stored in the database. Default option in queue mode.s3: Binary data is stored in S3 compatible store.
The N8N_AVAILABLE_BINARY_DATA_MODES setting will also be removed, so the mode is now determined only by N8N_DEFAULT_BINARY_DATA_MODE.
Migration path: Filesystem or database mode will be used automatically based on configuration. Make sure your n8n instance has enough disk space to store binary data. For details, see the binary data configuration.
Configuration & Environment#
Upgrade dotenv#
n8n loads environment configuration from a .env file using the dotenv library. The library will be upgraded from version 8.6.0 to the latest version, which may change how .env files are parsed. Key breaking changes include:
- Backtick support (#615): If your values contain backticks, wrap them in single or double quotes.
- Multiline support: You can now use multiline values.
#marks the beginning of a comment: Lines starting with # are treated as comments.
Migration path: Review the dotenv changelog and update your .env file to ensure compatibility with the new version.
Remove n8n --tunnel option#
The n8n --tunnel command-line option will be removed in v2.0.
Migration path: If you currently use the --tunnel option for development or testing, switch to an alternative tunneling solution such as ngrok, localtunnel, or Cloudflare Tunnel. Update your workflow and documentation to reflect this change.
Remove QUEUE_WORKER_MAX_STALLED_COUNT#
The QUEUE_WORKER_MAX_STALLED_COUNT environment variable and the Bull retry mechanism for stalled jobs will be removed because they often caused confusion and didn't work reliably.
Migration path: Delete this environment variable from your configuration. After upgrading, n8n will no longer automatically retry stalled jobs. If you need to handle stalled jobs, consider implementing your own retry logic or monitoring.
Remove N8N_CONFIG_FILES#
The N8N_CONFIG_FILES environment variable has been removed.
Migration path: Delete this environment variable from your configuration. Move configuration into environment variables, an .env file or _FILE based configuration.
CLI & Workflow#
Replace CLI command update:workflow#
The update:workflow CLI command will be deprecated and replaced by two new commands to deliver similar functionality and more clarity:
publish:workflowwith parametersidandversionId(optional)- The
--allparameter will be removed to prevent accidental publishing of workflows in production environments unpublish:workflowwith parametersidandall
Migration path: Use the new publish:workflow command to publish workflows individually by ID, optionally specifying a version. For unpublishing, use the new unpublish:workflow command. This provides better clarity and control over workflow publishing states.
External Hooks#
Deprecated frontend workflow hooks#
The hooks workflow.activeChange and workflow.activeChangeCurrent will be deprecated. These will be replaced by a new hook workflow.published. The new hook will be triggered when any version of a workflow is published.
Migration path: Update your code to use the new workflow.published hook instead of workflow.activeChange and workflow.activeChangeCurrent. This hook provides more consistent behavior and will be triggered whenever a workflow version is published.
Release channels#
n8n has renamed the release channels from latest and next to stable and beta, respectively.
The stable tag designates the latest stable release, and the beta tag designates the latest experimental release. These tags are available on both npm and Docker Hub. For now, n8n will continue to tag releases as latest and next. These tags will be removed in a future major version.
Recommendation: Pin your n8n version to a specific version number, for example, 2.0.0.
Reporting issues#
If you run into any problems while updating to n8n 2.0, visit the community forum for help and support.