Vector Store Question Answer Tool node#
The Vector Store Question Answer node is a tool that allows an agent to summarize results and answer questions based on chunks from a vector store.
On this page, you'll find the node parameters for the Vector Store Question Answer node, and links to more resources.
Examples and templates
For usage examples and templates to help you get started, refer to n8n's Vector Store Question Answer Tool integrations page.
Parameter resolution in sub-nodes
Sub-nodes behave differently to other nodes when processing multiple items using an expression.
Most nodes, including root nodes, take any number of items as input, process these items, and output the results. You can use expressions to refer to input items, and the node resolves the expression for each item in turn. For example, given an input of five name values, the expression {{ $json.name }} resolves to each name in turn.
In sub-nodes, the expression always resolves to the first item. For example, given an input of five name values, the expression {{ $json.name }} always resolves to the first name.
Node parameters#
Description of Data#
Enter a description of the data in the vector store.
Limit#
The maximum number of results to return.
How n8n populates the tool description#
n8n uses the node name (select the name to edit) and Description of Data parameter to populate the tool description for AI agents using the following format:
Useful for when you need to answer questions about [node name]. Whenever you need information about [Description of Data], you should ALWAYS use this. Input should be a fully formed question.
Spaces in the node name are converted to underscores in the tool description.
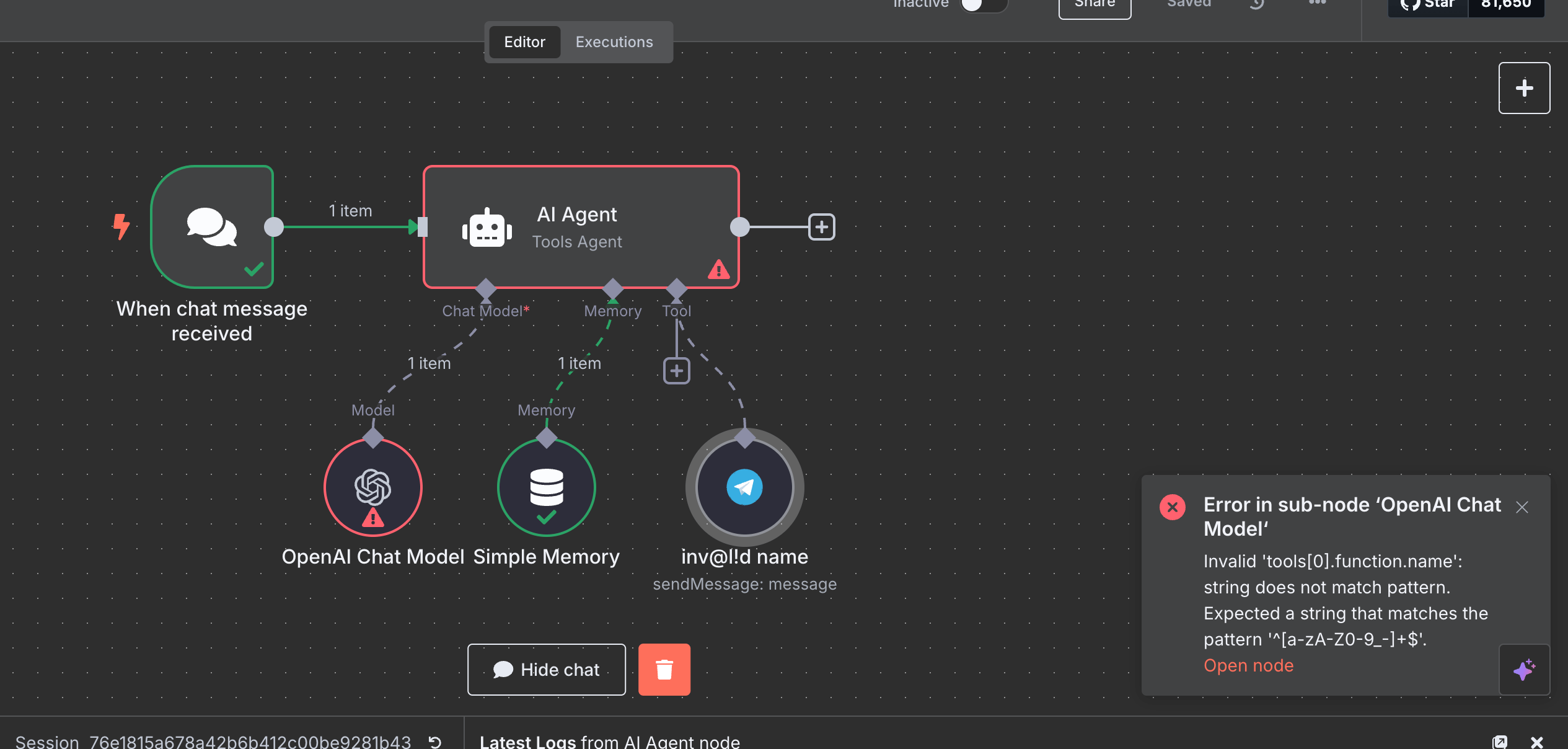
Avoid special characters in node names
Using special characters in the node name will cause errors when the agent runs:
Use only alphanumeric characters, spaces, dashes, and underscores in node names.
Related resources#
View example workflows and related content on n8n's website.
Refer to LangChain's documentation on tools for more information about tools in LangChain.
View n8n's Advanced AI documentation.